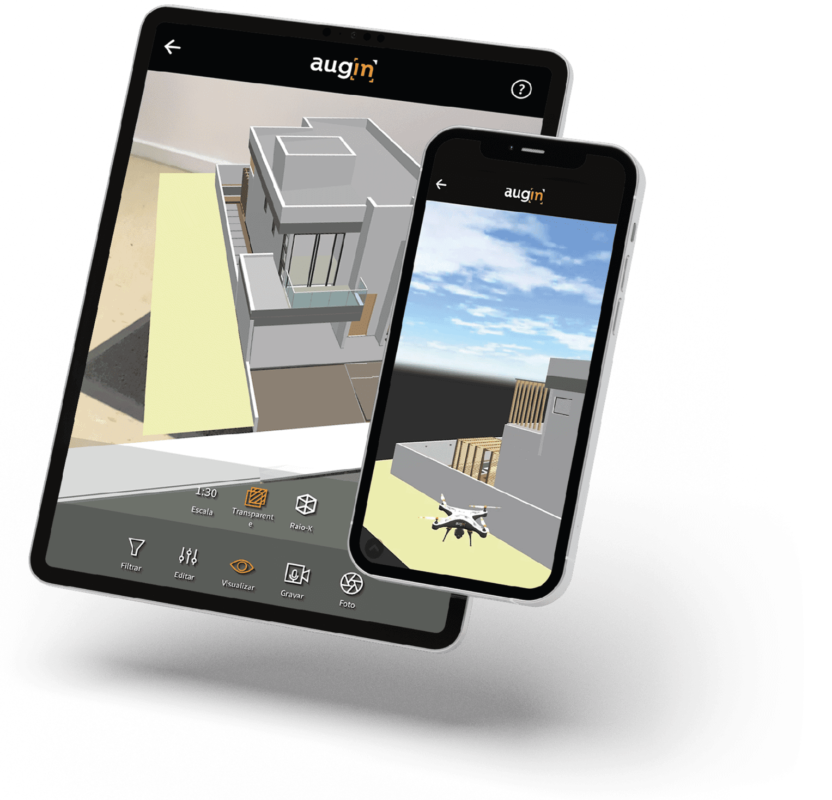
In recent years, Augmented Reality (AR) technology has gained traction in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. By blending digital content such as 3D models with the physical world, AR is reshaping how professionals approach design and construction processes.
Let’s take a closer look at how AR is making waves in the industry, helping construction companies bring new possibilities to the table.
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) is an immersive technology that overlays digital information, such as images and 3D models, onto real-world environments in real time, enabling users to experience both the digital and physical worlds simultaneously.
Visualization and Design Exploration
AR’s ability to enhance visualization is reshaping the design exploration phase. Designers and architects can now overlay intricate digital models onto real-world settings, providing them with a more holistic understanding of how their designs will interact with the physical environment. This advanced visualization capability not only aids in refining designs but also allows for better-informed decision-making early in the design process.
Moreover, AR facilitates immersive experiences, allowing stakeholders to interact with 3D models and virtual prototypes in real-time. This interactive approach fosters creativity and innovation, enabling designers to experiment with different design elements and configurations effortlessly.

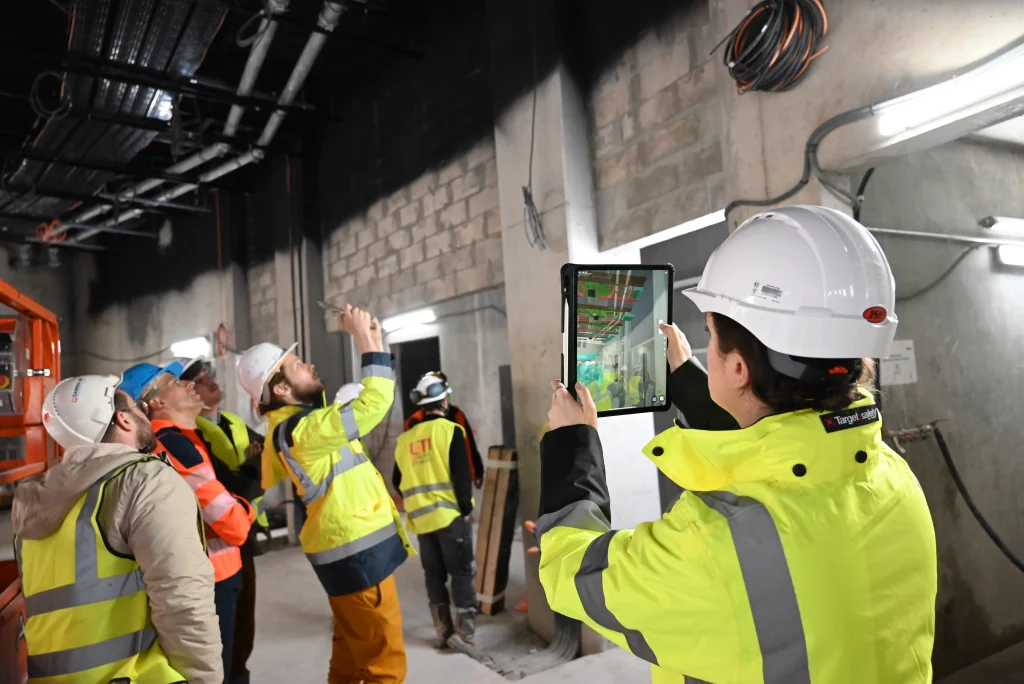
On-Site Construction Visualization and Planning Made Easy
On construction sites, AR technology is proving to be a valuable asset for visualization and planning tasks. By leveraging AR-enabled devices such as tablets or smart glasses, construction teams can superimpose digital models directly onto the physical construction site. This allows stakeholders to visualize how building components will integrate with existing structures and surroundings, facilitating more accurate planning and coordination.
Furthermore, AR enhances on-site communication by providing stakeholders with instant access to relevant project information and design data. This real-time collaboration fosters proactive decision-making and helps mitigate potential issues before they escalate, ultimately leading to smoother project execution and improved project outcomes.
Collaboration and Communication
AR serves as a catalyst for collaboration among project stakeholders, irrespective of their physical location. By providing a shared platform for visualizing designs and exchanging ideas, AR fosters seamless collaboration throughout the project lifecycle. Designers, architects, engineers, contractors, and clients can all view and interact with the same digital models in real-time, facilitating more efficient communication and reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Moreover, AR promotes inclusivity by democratizing access to project information. Stakeholders from diverse backgrounds and disciplines can contribute their expertise and insights, leading to more comprehensive and well-informed decision-making processes.
Safety and Training Reinvented
In the realm of safety and training, AR technology is redefining traditional approaches. By overlaying digital safety information and procedural instructions onto the physical workspace, AR helps construction workers identify potential hazards and adhere to safety protocols more effectively. This augmented safety awareness helps reduce the risk of workplace accidents and injuries, creating safer working environments for construction professionals.
Additionally, AR-based training simulations provide workers with realistic scenarios to practice essential tasks and procedures in a virtual environment. This immersive training experience enhances skill development and retention, ensuring that project teams are adequately prepared to tackle challenges on-site.
Technologies Supporting AR in Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM enables various teams involved in a construction project to create and share 3D design models into a single database (Common Data Environments), promoting and collaboration among stakeholders.
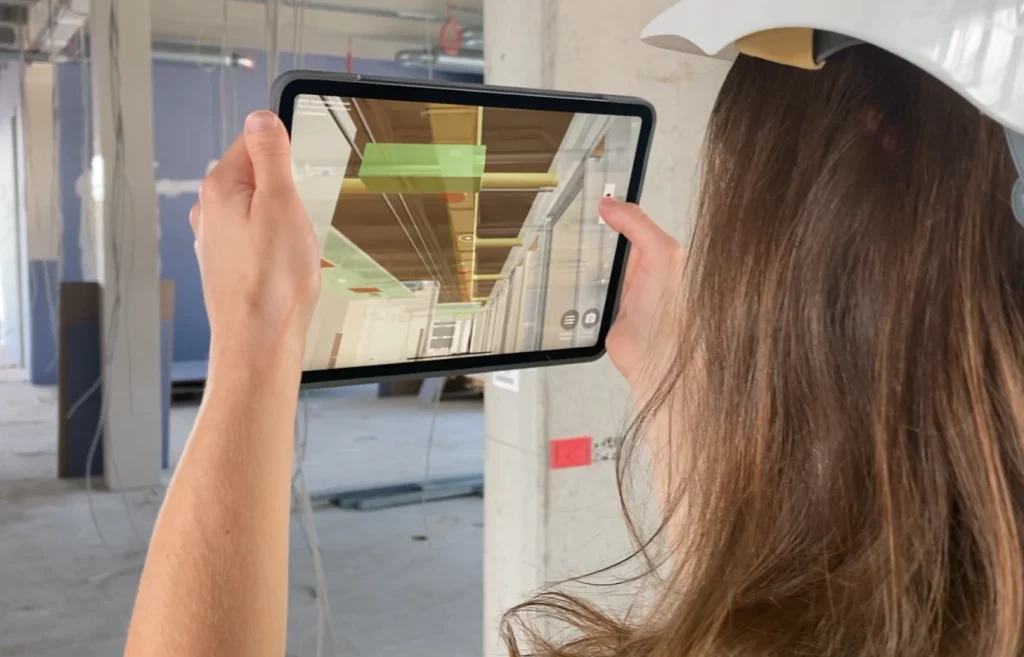
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) with BIM allows for BIM Models to be overlaid with a users view of the real world, creating a composite image that aids in on-site management and inspections. Combining Virtual models and real-world objects allows for a critical review of construction accuracy and progress.
AR Hardware Devices
AR applications enable users to view and interact with 3D models overlaid on real-world scenes, enhancing comprehension and visualization on construction sites.
HMDs (Head-Mounted Displays) typically feature advanced tracking technology, allowing for precise alignment of virtual imagery with the real world for enhanced immersion and user comfort.
Modern smartphones, tablets and mobile devices leverage advancements such as enhanced imaging capabilities and powerful processing units to support sophisticated AR applications in construction environments.
Challenges in Implementing AR
Skills Gap and Training
The construction industry faces a significant shortage of skilled workers, particularly those proficient in extended reality (XR) technologies, which hampers the effective utilization of these advancements.
Resistance to Adoption
Major challenges to the successful integration of AR in the construction sector include the accuracy of tracking and positioning augmented design visualizations at construction sites, which can hinder adoption.
Precise positioning is essential in construction; deviations between as-built and as-planned situations due to inaccurate AR visualizations can create reluctance to adopt the technology.
Looking Ahead: Future Possibilities
As AR technology continues to evolve, its potential applications in the design and construction sector are expanding. Future developments may include the integration of AR with advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, enabling seamless data exchange and visualization. Wearable AR devices, such as augmented reality glasses, hold promise for hands-free interaction with digital worlds and data visualization on construction sites, further enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms within AR environments could revolutionize real-time analysis and decision support capabilities. By leveraging AI-driven insights, stakeholders can make more informed decisions, optimize project workflows, and anticipate potential challenges proactively.
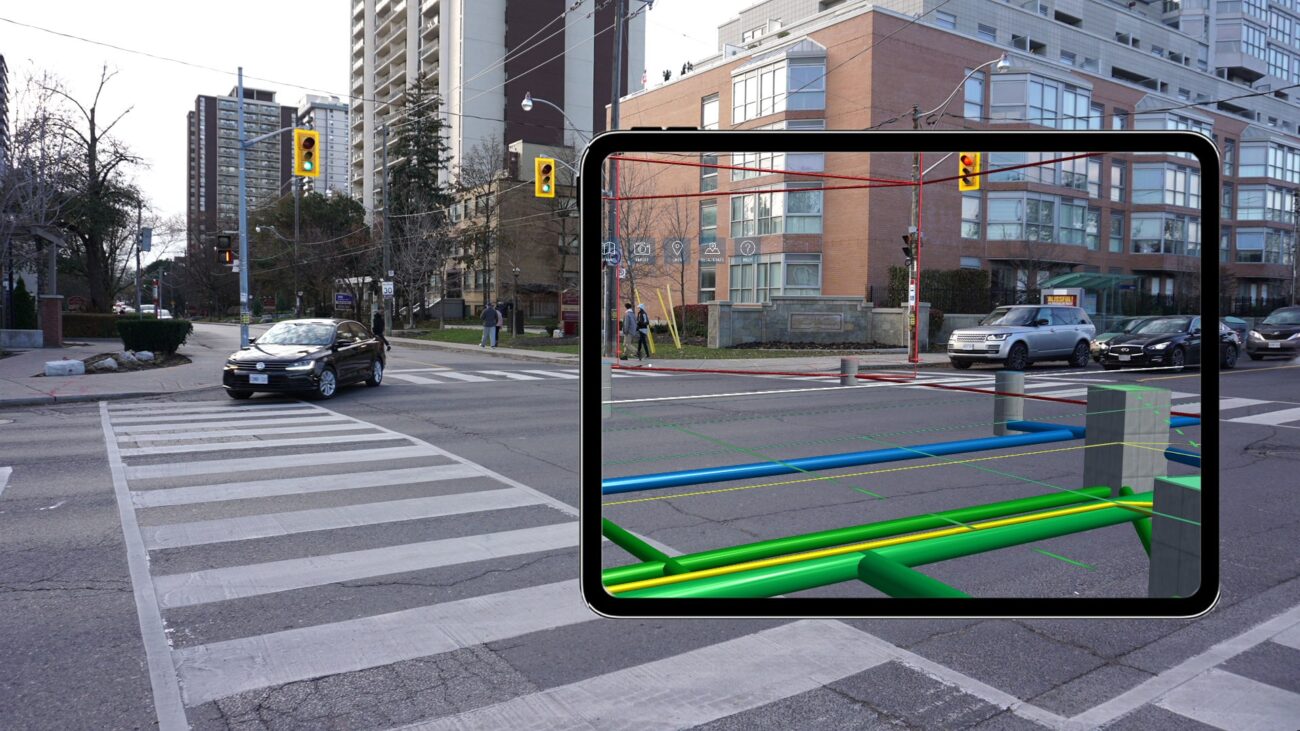

In Conclusion
Augmented Reality is undeniably reshaping the design and construction industry, offering transformative solutions for visualization, collaboration, safety, and training.
As professionals continue to explore and harness the capabilities of AR technology, the industry stands poised for unprecedented innovation and growth. With its potential to combine the design phase with real-time information, improve safety practices, and drive project efficiencies, AR is set to become an indispensable tool in the future of design and construction.